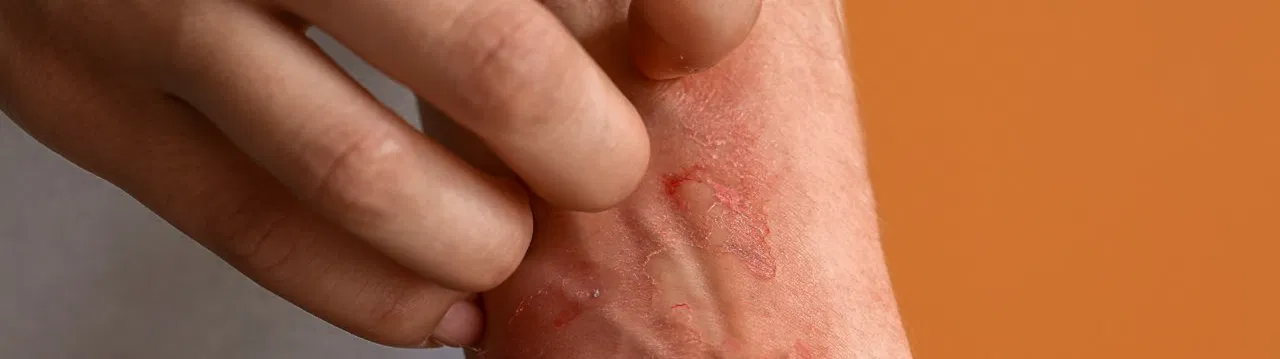
There are many types of eczema. They manifest themselves as red spots or spots, bumps, blisters, flaking and/or local swelling that are not contagious. The rash is the visible part of eczema, but the itching that almost always accompanies it and that can be severe is invisible. There is also a psychological aspect, people can feel insecure and ashamed of the damaged, disfiguring skin. Eczema treatments like and eczema cream is aimed at reducing eczema and itching and, if necessary, providing psychological support.
Eczema
Treatments
- All treatments
- Prescription medicines
- Non-prescription medicines
- Relevance
- Name A-Z
- Name Z-A
- Price low-high
- Price high-low


















How does Dokteronline work?
At Dokteronline, you can get expert advice from doctors quickly, without the hassle of visiting your GP’s surgery. Take care of your health with reliable treatments and information from the comfort of your home.
Select your preferred treatment
The doctor will review your medical request
The pharmacy will ensure your medication is delivered to your doorstep
What is eczema?
Eczema is a chronic non-contagious skin condition caused by an inflammatory skin reaction. This causes red flaky spots, bumps, swelling, fissures or crusts. Sometimes the results are also wet. Eczema is often accompanied by severe itching and is usually treated with an eczema cream.
What is the cause of eczema?
The following causes and factors influence eczema:
- Predisposition (it is in the family): this is the main cause;
- Climate factors: such as dry air, and/or cold air;
- Disease;
- Stress and tension;
- Skin bacteria;
- Chemicals such as skincare products;
- Dishwashing detergents;
- Sweating;
- Certain types of textiles: such as wool and/or nylon;
What forms of eczema exist?
There are different forms of eczema. The most common are:
- Constitutional or atopic eczema;
- Seborrheic eczema;
- Contact eczema;
- Dyshidrosis or blisters of eczema;
- Nummular eczema;
- Tylotic eczema;
- Eczema craquelé or asteatotic eczema;
- Hypostatic eczema;
How do you recognise eczema?
Depending on the form of eczema, the expressions and the location are different. Below are the phenomena per eczema form.
Constitutional or atopic eczema:
This is the most common form. This eczema has a hereditary component.
Eczema can be recognised as follows:
- It can occur anywhere on the body
- It is accompanied by (extreme, maddening) itching
- It can develop in infancy (acne) but is not age-related
- It causes redness, swelling, blisters, bumps, wetting, scabs, flaking and coarsening of the skin In adults, in the elbow folds, hollows of the knees, on the hands and feet
It has a variable course. Generally, you have dry skin
Seborrheic eczema:
This eczema is common. It is more common in men than in women. The symptoms are: Itching or yellowish spots that flake.
Often you’ll find this type of eczema for face complaints, on the nose, on the head, eyebrows, eyelashes, beard area, or around the ears.
It worsens with stress, cold and drought.
Eczema scalp gets worse by wearing headgear, like hats.
Contact eczema:
This eczema can be divided into allergic contact eczema and irritant contact eczema. With allergic contact eczema, a certain product can cause an allergy immediately or over time. The allergic reaction can spread to the body.
Many products can cause contact eczema: perfume, make-up, jewellery, latex (gloves), flowers, hair products. Some professions (hairdressers, healthcare workers, cleaners, etc.) have a higher risk of contracting eczema. Irritative contact eczema is caused by repeated contact with (often) water and soap or another wet product. Some products, in combination with sunlight, give the so-called photoallergic contact eczema (this can be the case with some medicines, perfumes, sunscreens.).
The symptoms of contact eczema are:
- Red itchy rash with flakes, bumps, blisters, fissures or crusts where the skin has been in contact with the product;
- Sometimes the skin is swollen.
Dyshidrosis or blisters of eczema:
This eczema is sometimes the result of a fungal infection of the feet or in the groin. The characteristics are: itchy clear blisters and sometimes even large blisters in the palms of the hands, between the fingers and/or soles of the feet and toes.
Nummular eczema:
This is a chronic form of eczema. It is characterised by:
- Coin-shaped red flaky patches, flaky lumps that can converge to larger patches;
- Sometimes crusts with cracks;
- Mostly on the legs;
- Occurs in young adults, earlier in women;
- With elderly people, more likely to occur in men;
- Occurs more frequently during the cold months.
Tylotic eczema:
Tylotic eczema is a chronic form of hand eczema. Its characteristics are:
- Calluses on the palms of the hands and the bending side of the fingers;
- Small, painful cracks;
- Often at the soles of the feet;
- Mostly in men.
Eczema craquelé or asteatotic eczema:
The characteristics are:
- Small cracks on (too) dry skin of the lower legs;
- Flaky skin;
- Pain and itching;
- Especially in older people;
- Exacerbation in dry periods of cold.
Hypostatic eczema:
This is caused by insufficient drainage of blood by the veins in the legs, resulting in varicose veins. As yet unknown, we see an inflammation that can cause eczema. The characteristics are:
- A damp rash on the lower legs Redness, scabs, flakes Swollen lower legs (oedema);
- Is particularly common among the elderly.
Is there anything I can do myself about eczema and itching?
Be aware that eczema is not contagious or dirty. You yourself can apply several precepts to combat eczema:
- Avoid scratching, no matter how hard it is. But scratching maintains or exacerbates the eczema;
- Keep your nails short;
- Keep an itching diary;
- Seek distraction when it is itchy;
- Make sure that the skin remains supple;
- Choose unscented skin products;
- Do not spend too long in the bath or shower and make sure the water is not too hot, lukewarm 37°C ;
- Do not use soap;
- Use neutral detergents;
- Wear airy cotton clothing, avoid wool and rough fibres, avoid synthetic clothing;
- Prevent stress.
What are the forms of eczema treatment?
Talk to a doctor. A doctor has a choice of several eczema treatments, depending of course on the type and severity of the eczema, the severity of the symptoms including the itching.
In eczema, the skin barrier is disturbed. The skin retains less moisture and dries out more quickly, which means that the skin is less protected against harmful substances. For mild forms of eczema, the doctor may choose a greasy ointment or eczema cream that does not contain any medication to increase the skin’s moisture content and make the skin less dry and supple again. Reduce flaming redness, chaps and itching. In the case of wet eczema, it is preferable to use an eczema cream, in the case of dry eczema it is preferable to use an ointment or fat cream.
The following eczema creams or ointments can be considered:
- Cetomacrogol cream FNA (wet eczema);
- Lanette cream FNA;
- Vaseline cetomacrogol cream FNA;
- Cetomacrogol ointment FNA;
- Vaseline relief cream FNA;
- Lanette ointment FNA (dry eczema);
- Cooling ointment FNA;
- Paraffin/vaseline ointment FNA
If the non-medicinal ointments and eczema creams do not help enough, a combination of these products will be used.
In the case of seborrheic eczema scalp on the head or beard, a mild shampoo with zinc pyrithione or piroctone could be chosen first. The use of cosmetics is not recommended. Do not wear headgear, as exposure to sunlight is good, but watch out for sunburn.
With contact eczema, it is important to find out which product causes the eczema. For example, nickel in jewellery or perfume, then it is easy to avoid these products. If dyshidrosis is caused by a fungal infection elsewhere in the body, eczema can disappear if the fungal infection is treated.
In hypostatic eczema, compression stockings will help to counteract the fluid in the legs (oedema).
Medication
If the non-medicinal ointments and creams do not help sufficiently, a moderate form of eczema will require local therapy with corticosteroids from the lowest possible class. These are divided into 4 classes according to strength: class 1 is the lightest, class 4 the strongest.
In the case of wet eczema it is preferable to use a cream-based corticosteroid in the case of dry eczema an ointment or fat eczema cream should be preferred:
- Hydrocortisone eczema cream/lubricant/vaseline cream FNA (acetate);
- Hydrocortisone eczema cream/ointment FNA.
Hydrocortisone eczema ointment, 2 times a day
The advantage of the simultaneous use of an eczema cream or ointment is that fewer corticosteroids need to be used. These products are used for a short period of 1 to 2 weeks (except in case of recurrent eczema) after which the treatment with hydrocortisone ointment or hydrocortisone eczema cream is discontinued.
In case of insufficient effect, localised eczema treatment therapy with one of the following class 2 corticosteroids will be chosen:
- Clobestane Llumetasone Hydrocortisone butyrate;
- Triamcinolon acetonide (dermatological).
Again in combination with a fatty ointment or eczema cream without hydrocortisone. If there is an insufficient effect, a class 3 corticoid will be used.
In case of severe eczema, the doctor can choose one of the local class 3 corticosteroids and an eczema cream or ointment without hydrocortisone:
- Betamethasone (dermatological) Desoximetasone;
- Fluticasone (dermatological) Mometasone (dermatological).
When improved after 1 to 2 weeks, the corticosteroids are discontinued.
When resistance to corticoids has occurred in constitutional eczema or contact eczema, it is possible to choose:
- Elidel Protopic.
For seborrheic eczema:
If the eczema does not diminish with the non-medicinal eczema treatment, one of these eczema treatments may be chosen until the crusts or flaking have disappeared:
- Ketoconazole eczema cream, has an unpleasant odour and can cause hair loss and hair colouration;
- Selenium sulphide, only on hairy scalp.
If necessary, urea or salicylic acid can be added to make thick crusts disappear more quickly. They should not be used on eyes or mucous membranes.
Alternative treatments
Eczema reams (without a doctor’s prescription) based on chamomile, liquorice and witch hazel counteract inflammation of the skin and could possibly be used. Echinaforce cream works well as an eczema cream as it is also anti-inflammatory and reduces scarring. Menthol ointment has a cooling effect and can help against itching. You can also wrap a cold pack in a cloth and lay it on the spot that itches or is painful. Never place a cold pack directly on the skin, as it can stick to the skin. You can keep an itching diary to deal with the itching better. You can do this under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
You may also benefit from relaxation exercises to reduce itching.
Lifestyle changes
Live as healthily as possible. Avoid stress, get a good night’s sleep. Do not drink too much alcohol, do not smoke. Eat healthily. Do not shower for too long. Dab your skin after showering. Do not use aggressive lotions or soap.
Additional risks and side effects
Due to scratching a lot, the skin can be scratched open. This could cause infection. Corticosteroids can make the skin thinner and leave stretch marks, and the skin can also become lighter in colour. This can be experienced as disfiguring and can be accompanied by feelings of insecurity.
How can you prevent eczema and itching?
By applying the right precepts (see “Can I do something myself about eczema and itching”), you can prevent eczema and itching or give it less of a chance. Keep your skin supple by using an eczema cream or ointment (see “Most mild forms of eczema”) or any other unscented cream. Consult a doctor if you suffer from eczema again or if you experience more eczema.
References
huidarts.com (z.d.) dyshidrosis. (consulted on 25 April 2019). https://www.huidarts.com/huidaandoeningen/blaasjeseczeem- acrovesiculeus-eczeem/
huidarts.com (z.d.). seborrheic eczema. (consulted on 25 April 2019). https://www.huidarts.com/huidaandoeningen/seborrhoisch-eczeem-adulte-vorm/
huidinfo.nl (z.d.). Tylotic eczema. (consulted on 25 April 2019). https://www.huidinfo.nl/t/tylotisch-eczeem/ huidinfo.nl (z.d.). Hypostatic eczema (consulted on 25 April 2019). https://www.huidinfo.nl/h/hypostatisch-eczeem/
Huidfonds.nl (z.d.). Is there anything I can do myself about eczema? (consulted on 25 April 2019). https://huidfonds.nl/je- huid/huidaandoeningen/eczeem/
Mekkes, J.R. (03-06-2012) Nummular eczema. (consulted on 25 April 2019). https://www.huidziekten.nl/folders/nederlands/nummulair-eczeem.htm
Pharmacoterapeutic compass (s.d.) Seborrhagic, Contitutional, Contact eczema/treatment plan/medicines. (consulted on 25 April 2019). https://www.farmacotherapeutischkompas.nl/zoeken?domein=indicaties&alledomeinen_zoekterm=eczeem
Skin hospital dermicis (z.d.). Contact eczema. (consulted on 25 April 2019). https://www.dermicis.nl/nl/aandoeningen/eczeem/contacteczeem
Skin doctor (z.d.). Forms of eczema. (consulted on 25 April 2019). https://www.huidarts.com/huidaandoeningen/eczeem/ Tartuffel (2011) Eczema craquelé. (consulted on 25 April 2019). https://mens-en-gezondheid.infonu.nl/aandoeningen/79976- craquele-eczeem-asteatotisch-eczeem-symptomen-en-oorzaak.html